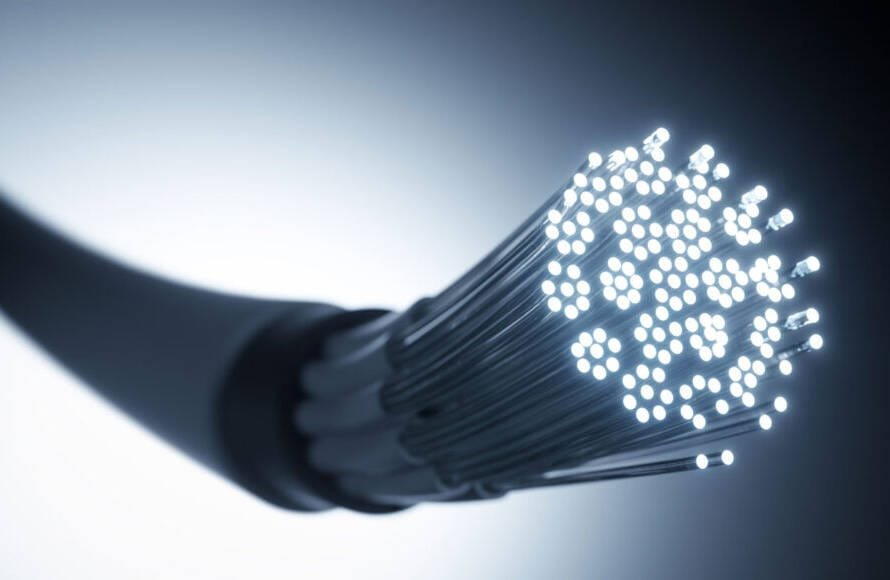
What is fiber?
Fiber, also known as fiber optics, consists of ultra-thin glass fibers that transmit Internet data over long distances at the speed of light. Thanks to the use of light pulses for data transport, fiber provides an unprecedentedly fast and extremely stable Internet connection. This technology is not only reliable, but also extremely secure and able to handle large amounts of data traffic effortlessly, making it ideal for modern digital applications.
Sending data over fiber, how does that work?
Having trouble imagining how a fiber cable transmits digital data via light? We understand that! Think of the principle of Morse code, where you transmit a unique message through flashes of light in a certain pattern. Fiber technology works the same way: data is transmitted via light pulses in unique patterns - where the light constantly goes on and off. The faster this "blinking" occurs, the more data can be transported per second.
Of course, these light signals are not simply converted into usable internet signals. To do this, you need a special fiber box at home or business, which takes over the function of your traditional modem. This box ensures that the light pulses be converted into the ultra-fast and stable Internet connection that fiber makes possible.
The difference with coax or copper
Today, data is still mostly transmitted via copper cables or coax, which operate with electromagnetic pulses. While these technologies were fine in the past, they were not originally designed to connect us to the Internet. As we engage in more and more online activities, the limitations of these traditional systems are beginning to become apparent. The capacity is often not sufficient for today's intensive data traffic, which can lead to slower connections and less stability, especially when using the Internet heavily or streaming heavy content.
If you use copper cable (VDSL or ADSL), your Internet connection runs through your telephone line. The further you live from the local exchange, the slower your connection and the less data you can send or receive. Copper is also sensitive to interference or damage from heavy rain or heat, for example.
Coax: internet through the television cable
If you use copper cable (VDSL or ADSL), your Internet connection runs through your telephone line. The further you live from the local exchange, the slower your connection and the less data you can send or receive. Copper is also sensitive to interference or damage from heavy rain or heat, for example.
Buyer: internet over the phone
If you use copper cable (VDSL or ADSL), your Internet connection runs through your telephone line. The further you live from the local exchange, the slower your connection and the less data you can send or receive. Copper is also sensitive to interference or damage from heavy rain or heat, for example.
The benefits of fiber
With fiber, each home has its own fiber cable, so it doesn't matter how many neighbors or roommates are online at the same time. Downloading a handful of movies in less than a second? Never get stuck in a video call again, even if the whole neighborhood is busy gaming or watching YouTube videos? With a fiber connection, your Internet is at any one time lightning fast and super-stable.